Template Strand In Dna
Template Strand In Dna - Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Dna replication in eukaryotes occurs in three stages: Replication creates identical dna strands, while transcription converts dna into messenger rna (mrna). Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). Transcription begins when rna polymerase binds to the dna template strand. Web in transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is rewritten in rna. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. During this step, rna polymerase and its associated. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication,. During this step, rna polymerase and its associated. Understand the difference between template and coding strands. Difference between coding strand and template strand. Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors (compared on page. Transcription begins when rna polymerase binds to the dna template strand. Memory anchors and partner content. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. In translation, the sequence of nucleotides in the mrna is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (protein chain). Initiation, elongation, and termination, which are aided by several enzymes. The term template strand refers to. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Understand the difference between template and coding strands. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template. Difference between coding strand and template strand. The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time. Understand the difference between template and coding strands. Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors (compared on page. Web in transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is rewritten in rna. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it. Dna serves as the molecular basis of heredity through replication, expression, and translation processes. Dna replication in eukaryotes occurs in three stages: An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. During this step, rna polymerase and its associated. Web what is the dna template strand? What is dna template strand? Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors (compared on page. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Initiation of protein synthesis p. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. An investigator is studying the transcription of. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Visit byju’s biology for more interesting topics. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors (compared on page. Web what is the dna template strand? Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Cells are able to repair dsbs by two major pathways: One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The first step in transcription is initiation. Initiation, elongation, and termination, which are aided by several enzymes. What is dna template strand? Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. If not repaired accurately and efficiently, this damage may lead to cell death or tumorigenesis. The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand.
Template Strand Of Dna

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Coding Versus Template Strand
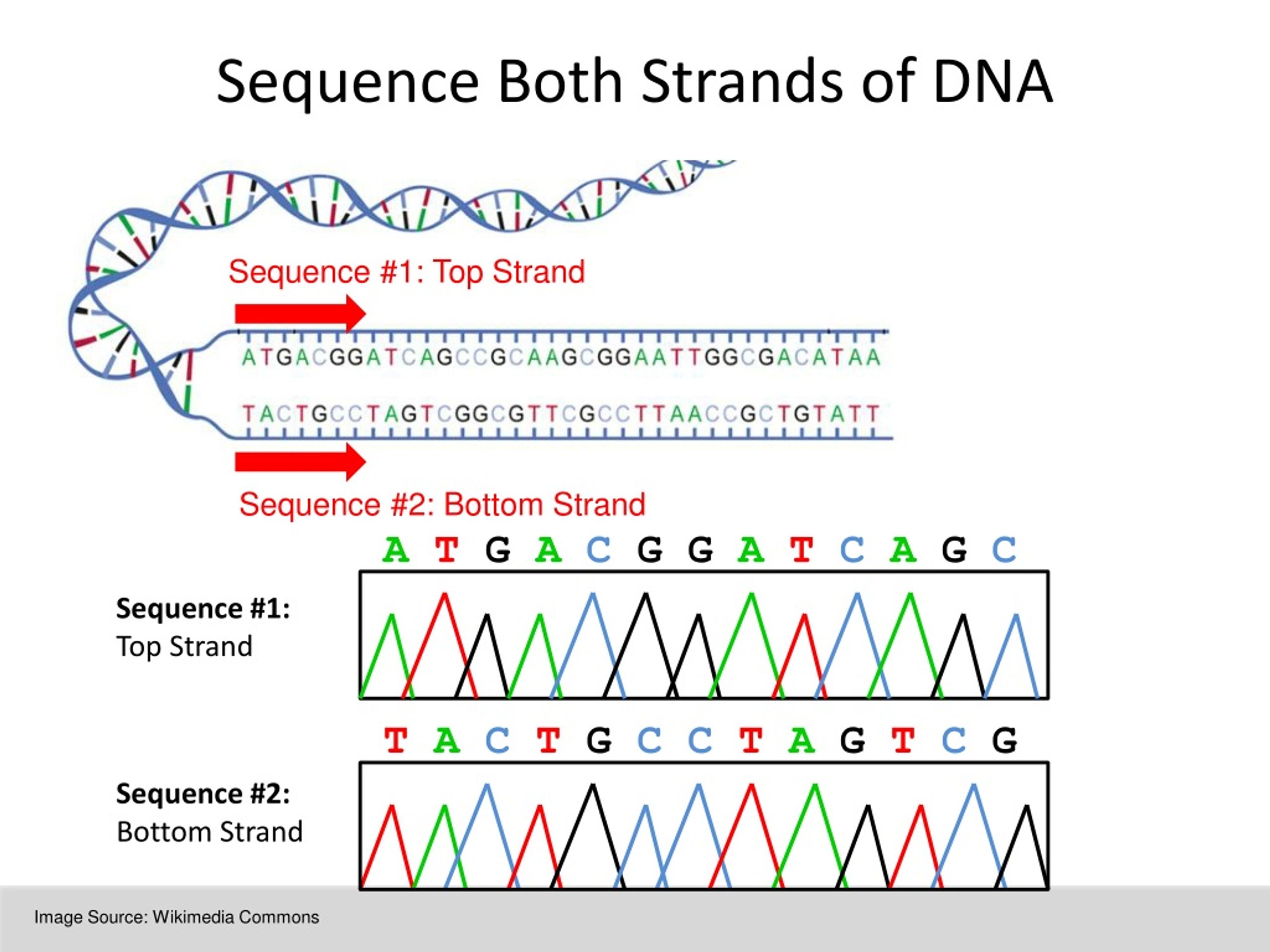
PPT LESSON 9 Analyzing DNA Sequences and DNA Barcoding PowerPoint

What strand of DNA is used to make a complementary copy or to make a

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial

replication Britannica

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
In Translation, The Sequence Of Nucleotides In The Mrna Is Translated Into A Sequence Of Amino Acids In A Polypeptide (Protein Chain).
Understand The Difference Between Template And Coding Strands.
Each New Double Strand Consists Of One Parental Strand And One New Daughter Strand.
Web In Transcription, The Dna Sequence Of A Gene Is Rewritten In Rna.
Related Post: