Smooth Muscle Tissue Drawing
Smooth Muscle Tissue Drawing - Web smooth muscle tissue contraction is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs. Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (figure 10.2). By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web definition / general. Like striated muscle, smooth muscle can tense and relax. It forms the contractile component of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems as well as the airways and blood vessels. Web describe a dense body. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are a lot smaller than cardiac muscle cells, and they do not branch or connect end to end the way cardiac cells do. Explain how smooth muscle works with internal organs and passageways through the body. Explain how smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. Web in this simple guide, i will show you the important identifying features of the smooth muscle fibers at a light microscope with the labeled diagram. 80k views 2 years ago. Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (figure 10.2). Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. Web smooth muscle can be confused with cardiac muscle because the cells are often running in different directions, just as they are in cardiac muscle. Web 12/05/2023 26/04/2021 by sonnet poddar. Smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle in function. Explain how smooth muscle works with internal organs and passageways through the body. Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. 1 of 3 types of muscle tissue alongside cardiac and skeletal muscle. Web in this simple guide, i will show you the important identifying features of the smooth muscle fibers at a light microscope with the labeled. It is found in numerous bodily systems, including the ophthalmic, reproductive, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems, where it functions to contract. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. Smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle in function. Web describe a dense body. Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. In relaxed smooth muscle, the nuclei are elongated with rounded ends. Web definition / general. The area inside the box is enlarged in the next image. Web explain the process of smooth muscle contraction. Web smooth muscle can be confused with cardiac muscle because the cells are often running in different directions, just as they are in cardiac muscle. How to draw a muscle tissue | straight muscles | smooth muscles | cardiac muscleshello friends in this video i tell you about how to draw labelled dia. Nonstriated muscle that serves diverse functions throughout the body and is responsible for involuntary movements. Web smooth muscle can be confused with cardiac muscle because the cells are often running in different. In this short guide, i will show you the different features of the smooth muscle histology slide. Web in this article, we'll go through the structure, function, location, characteristics, diagrams and examples of smooth muscle tissue. Web smooth muscle can be confused with cardiac muscle because the cells are often running in different directions, just as they are in cardiac. Web in this article, we'll go through the structure, function, location, characteristics, diagrams and examples of smooth muscle tissue. Web describe a dense body. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. Muscle is classified into three types according to their structure and function: Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing. Web muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body, and the body contains three types of muscle tissue: These muscles are found in almost all organs in the form of bundles or sheaths. In this short guide, i will show you the different features of the smooth muscle histology slide. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets. Web in this simple guide, i will show you the important identifying features of the smooth muscle fibers at a light microscope with the labeled diagram. In relaxed smooth muscle, the nuclei are elongated with rounded ends. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells do not exhibit striations since their actin and myosin (thin and thick) protein filaments. It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. They form the major contractile tissues of various organs. How to draw a muscle tissue | straight muscles | smooth muscles | cardiac muscleshello friends in this video i tell you about how to draw labelled dia. Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. Explain how smooth muscle works with internal organs and passageways through the body. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells do not exhibit striations since their actin and myosin (thin and thick) protein filaments are not organized as sarcomeres. These muscles are found in almost all organs in the form of bundles or sheaths. The area inside the box is enlarged in the next image. Explain how smooth muscle works with internal organs and passageways through the body. Explain how smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle. Web structure and function. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. In relaxed smooth muscle, the nuclei are elongated with rounded ends. Web in this simple guide, i will show you the important identifying features of the smooth muscle fibers at a light microscope with the labeled diagram. Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. It is found in numerous bodily systems, including the ophthalmic, reproductive, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems, where it functions to contract.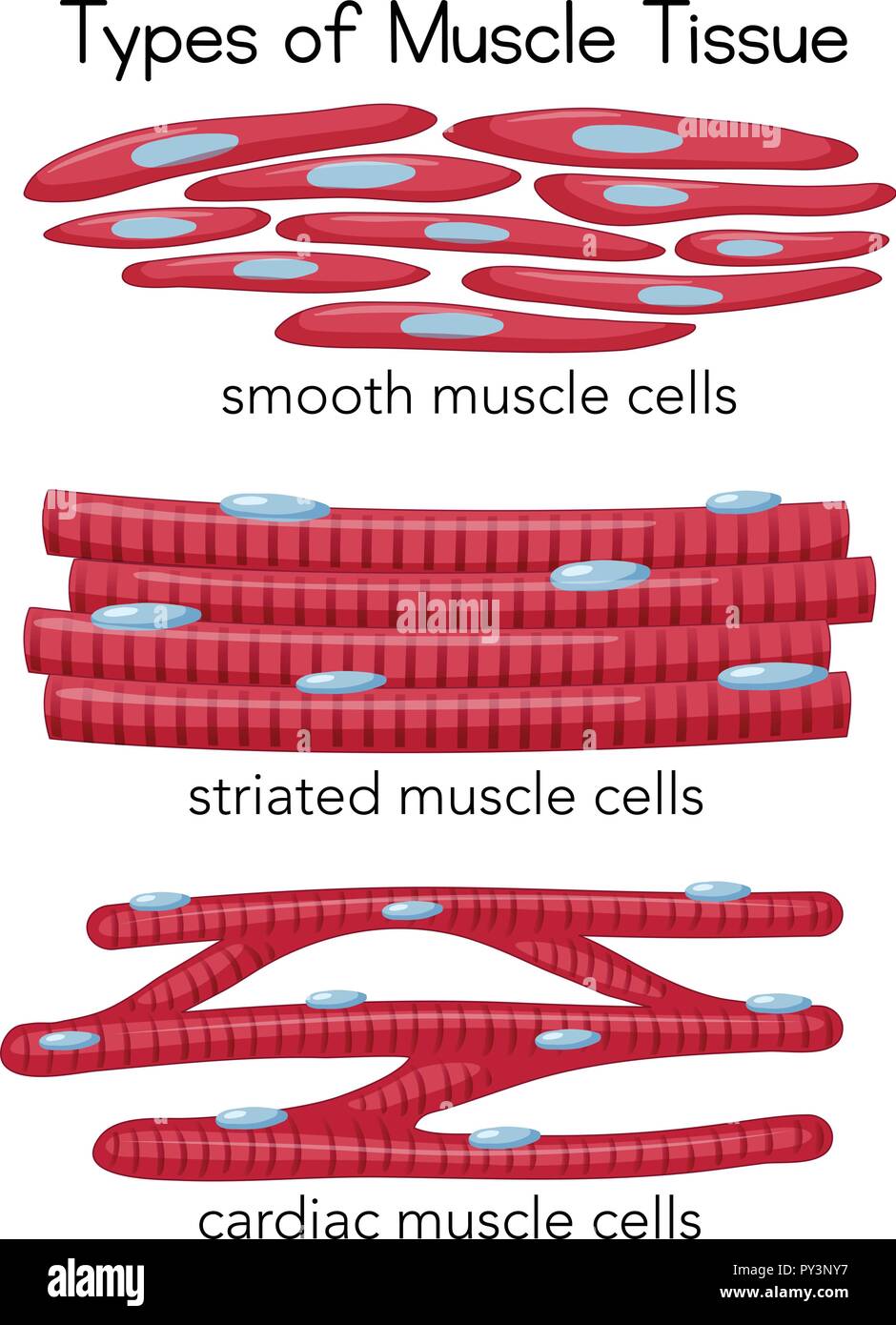
Smooth Muscle Tissue Telegraph

Smooth Muscle Tissue Diagram Labeled Tissue Photos An vrogue.co
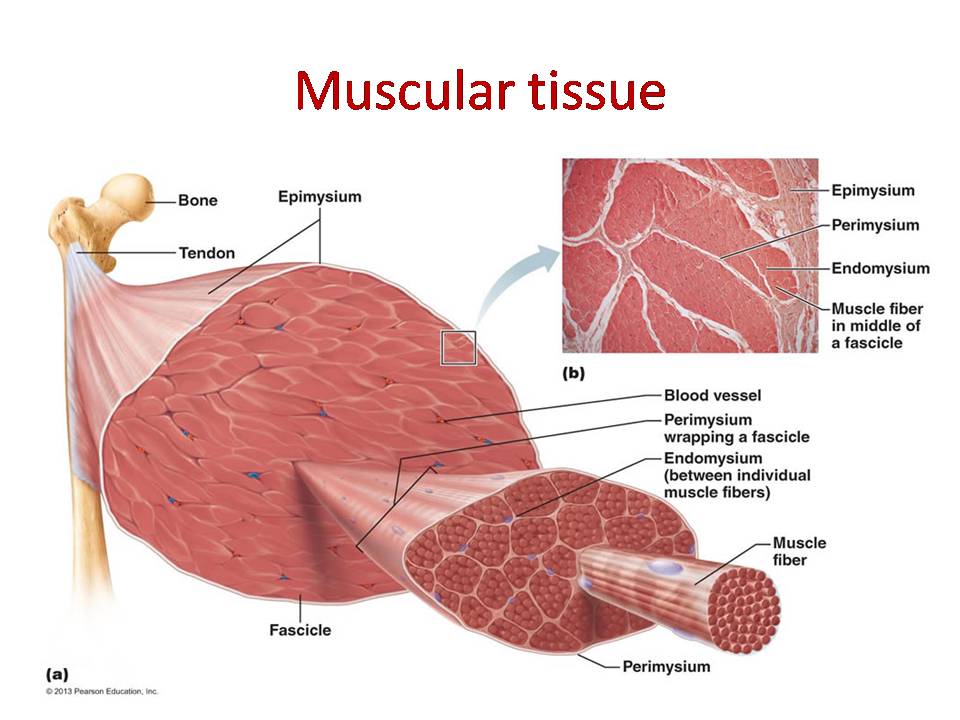
Muscle Tissue Diagram Labeled

Muscle Cell Drawing

10.8 Smooth Muscle Douglas College Human Anatomy and Physiology I
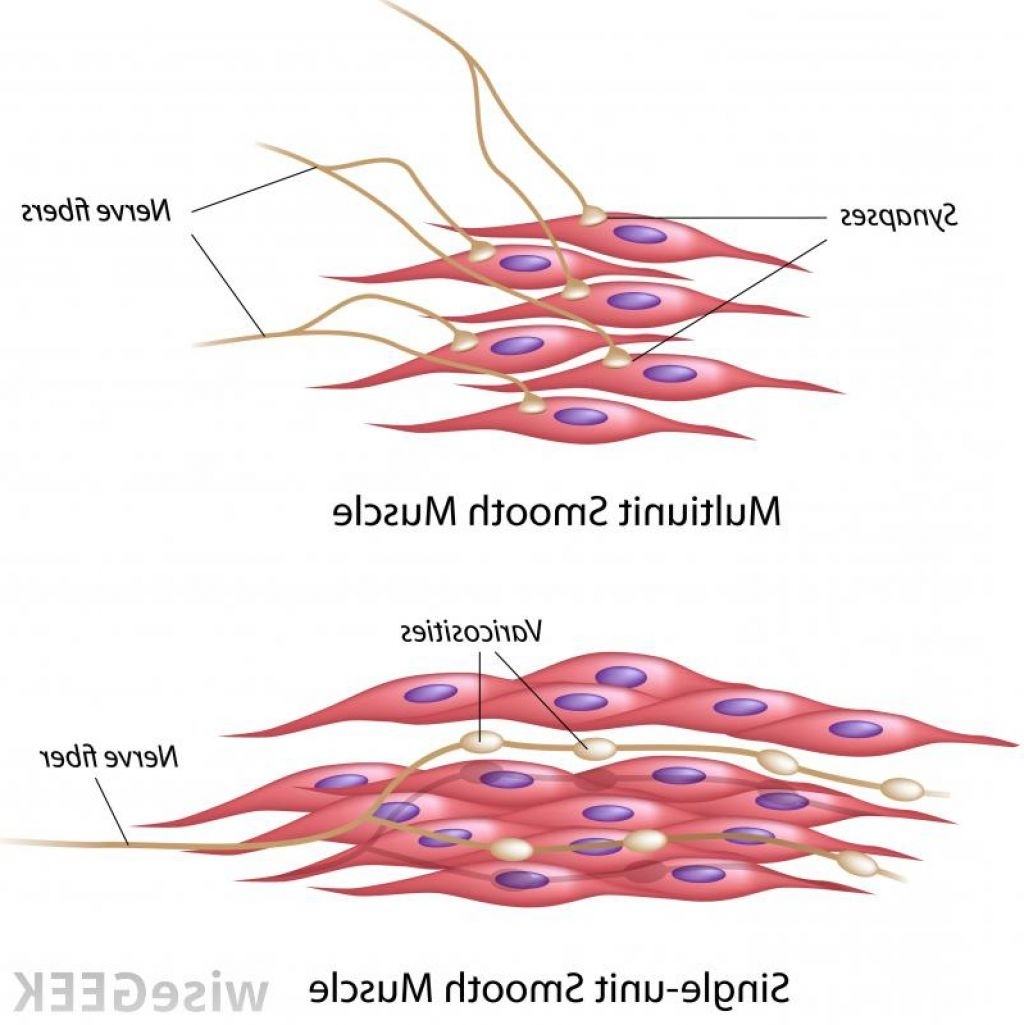
Smooth Muscle Tissue Diagram Labeled
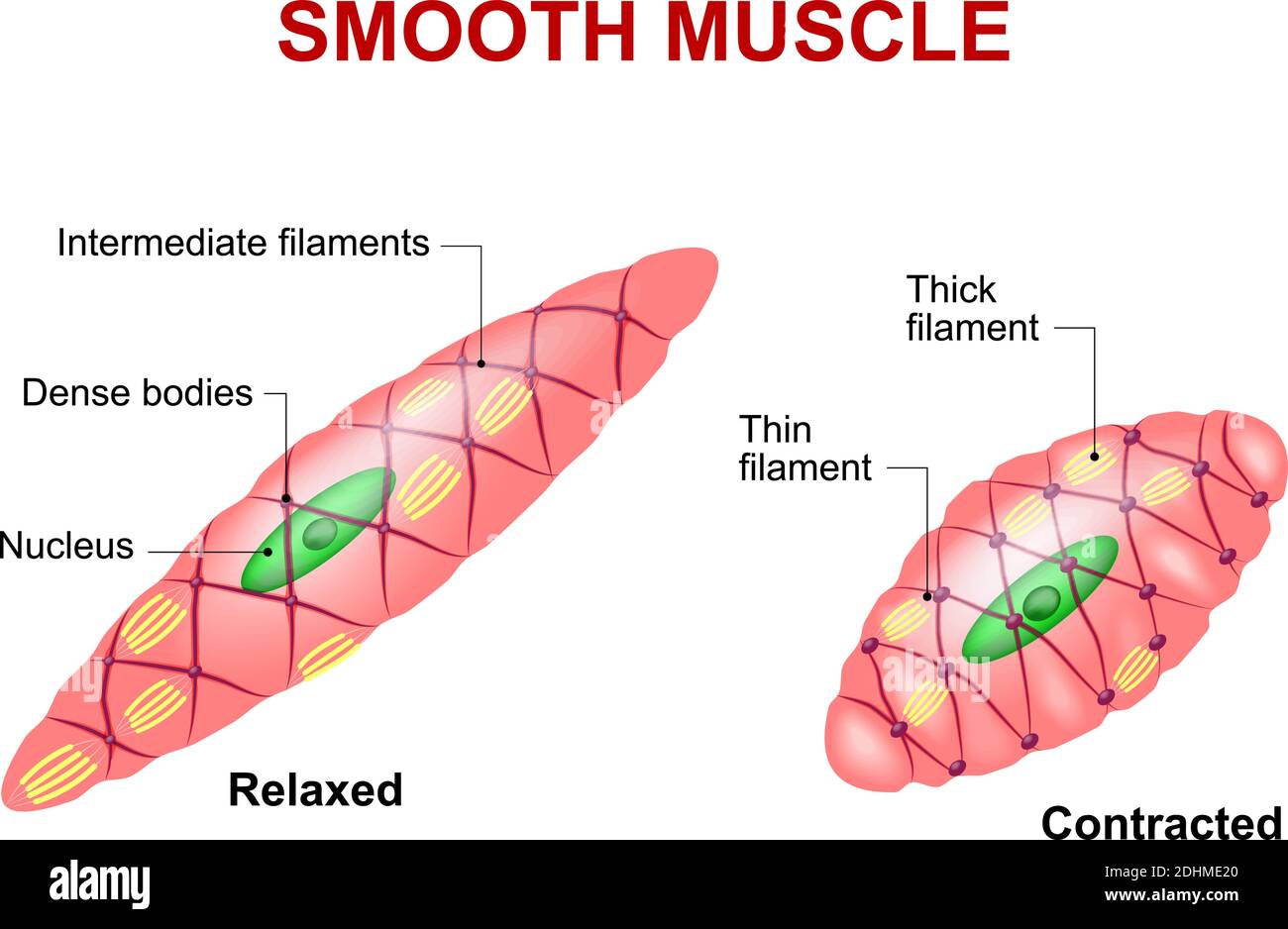
Smooth Muscle Tissue Anatomy
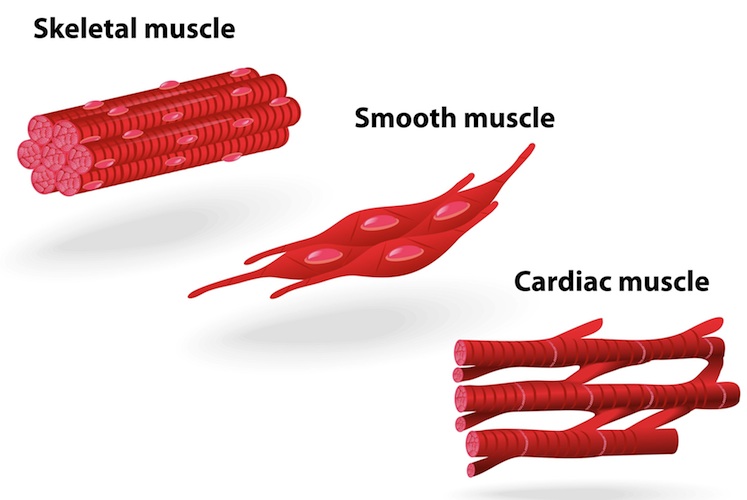
muscle tissue types diagram

LM of a section through human smooth muscle tissue Stock Image P154

Muscle tissue Medically
Smooth Muscle Cells Are A Lot Smaller Than Cardiac Muscle Cells, And They Do Not Branch Or Connect End To End The Way Cardiac Cells Do.
Web Describe A Dense Body.
Smooth Muscle Differs From Skeletal Muscle In Function.
Like Striated Muscle, Smooth Muscle Can Tense And Relax.
Related Post: