Serous Membrane Drawing
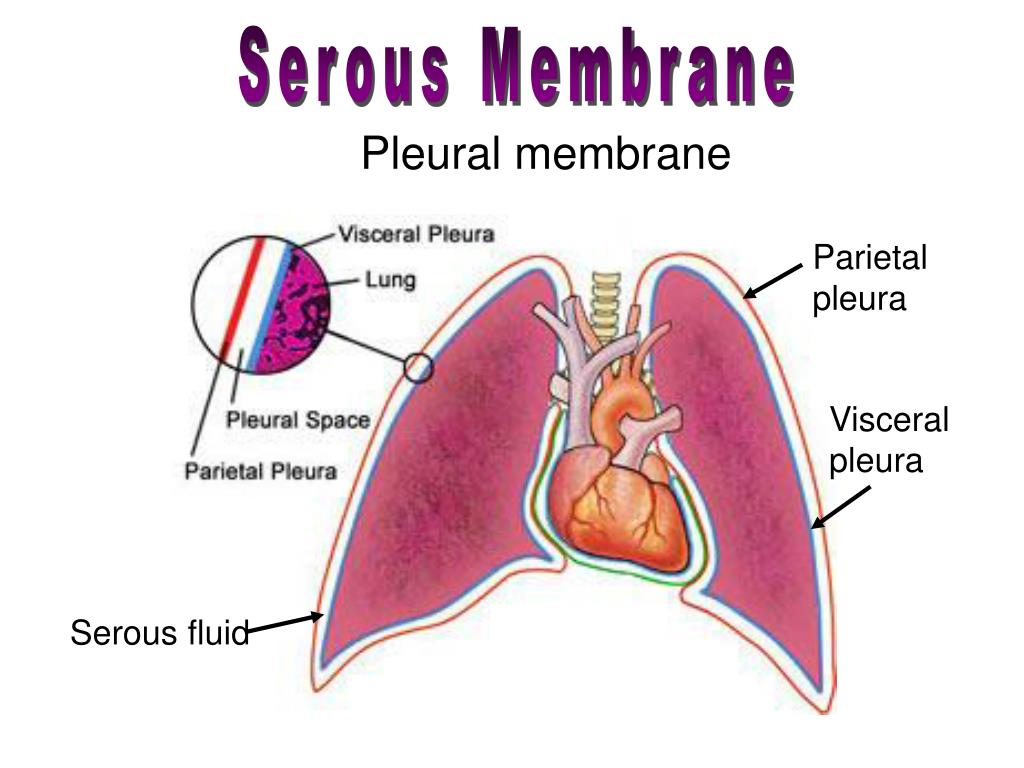
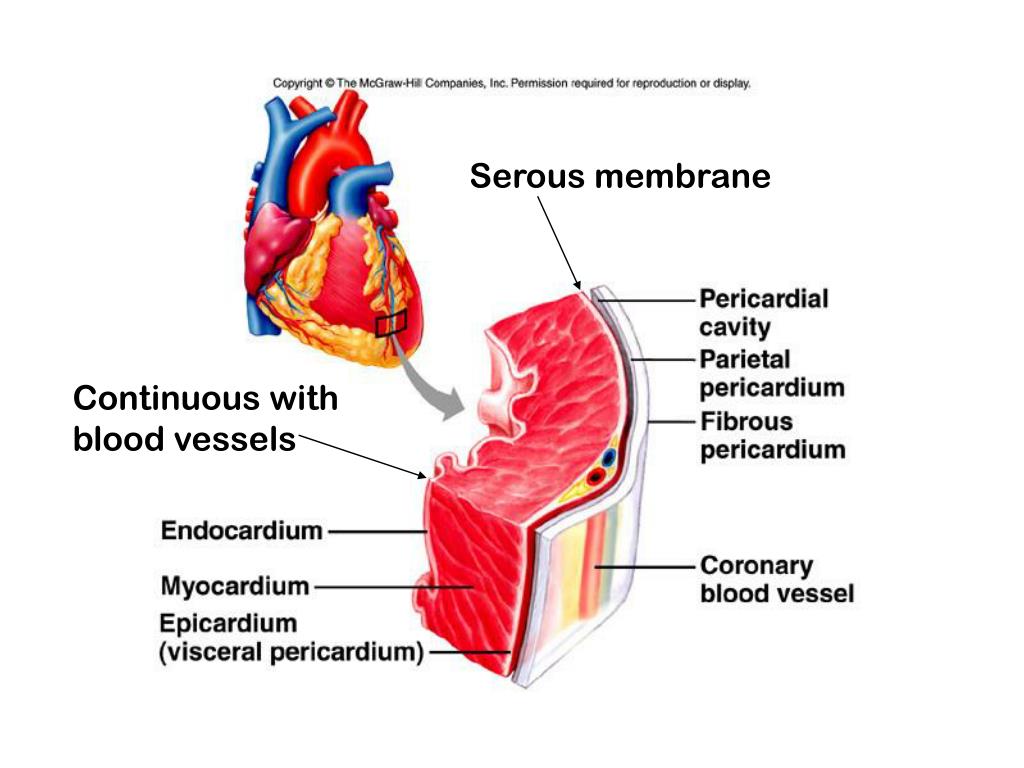
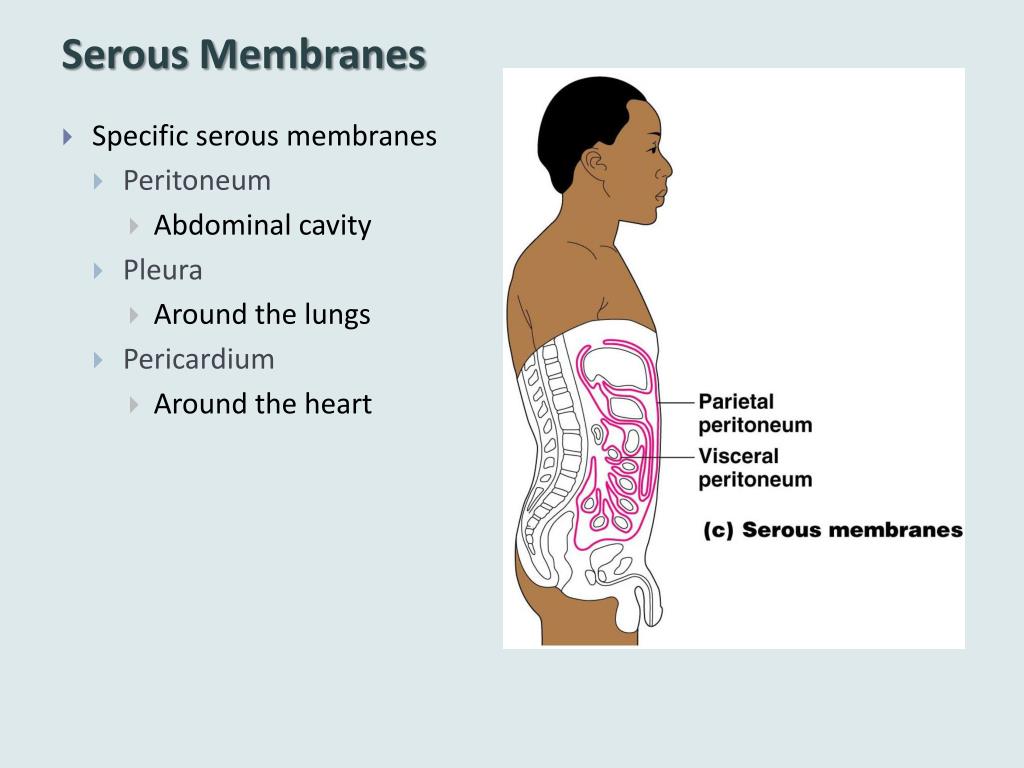
Serous Membrane Drawing - Web a serous membrane consists of a single layer of flattened mesothelial cells applied to the surface of a thin layer of collagenous tissue that attaches to underlying endothoracic/transversalis fascia. Histology of a serous membrane. The two pleura that cover the lungs and the pericardium that covers the heart. One is covering the outermost surface of the organ, and is call the visceral layer. Please leave a like and subscribe! The cells within a tissue share a common embryonic origin. The type of epithelium that lines the internal body cavities, is called mesothelium. Any serous membrane will always have two parts: Web a tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body (for example, skin), the organs (for example, pericardium), internal passageways that lead to the exterior of the body (for example, abdominal mesenteries), and the. Microscopic observation reveals that the cells in a tissue share morphological features and are arranged in an orderly pattern that achieves the tissue’s functions. Web the pleurae refer to the serous membranes that line the lungs and thoracic cavity. In histology this layer is called serosa after serous membrane. The type of epithelium that lines the internal body cavities, is called mesothelium. Regions, subdivisions of dorsal and ventral cavity revie. Any serous membrane will always have two parts: One associated with each lung. The largest part of the gut tube is ensheathed in peritoneum. The multicellular exocrine glands known as serous glands develop from simple epithelium to form a secretory surface that secretes directly into an inner cavity. The two pleura that cover the lungs and the pericardium that covers the heart. The cells within a tissue share. One is covering the outermost surface of the organ, and is call the visceral layer. Histologically, this can be seen as a layer on the outside of the gut. Web the serous membrane in the drawing above is composed of epithelium which is always simple squamous epithelium attached to a thin layer of connective tissue, which is always areolar connective. Web ⚡ welcome to catalyst university! Differentiate among the digestive organs and their location relative to. I am kevin tokoph, pt, dpt. Web the pleurae refer to the serous membranes that line the lungs and thoracic cavity. Histology of a serous membrane. The mesothelium of the serous membrane forms the lining of a closed serous membrane cavity. Web the serous membrane in the drawing above is composed of epithelium which is always simple squamous epithelium attached to a thin layer of connective tissue, which is always areolar connective tissue. Click the card to flip 👆. The largest part of the gut tube. They permit efficient and effortless respiration. Web this video shows how to complete a draw it activity for sketching body cavities and serious membranes within the chest. Any serous membrane will always have two parts: Anatomy and physiology is among the oldest of scientific disciplines. One associated with each lung. Any serous membrane will always have two parts: The outer layer ( parietal pleura) attaches to the chest wall. Web the unicellular glands are scattered single cells, such as goblet cells, found in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine. Created on january 18, 2021. The two pleura that cover the lungs and the pericardium that covers the. Serous membranes consist of a single layer of epithelium, named mesothelium, attached to a supporting layer of connective tissue, with a small layer in between, the basal membrane (fig 1). Web anatomy physiology of body cavities, serous membranes, and their contents explained, drawn, defined. They permit efficient and effortless respiration. There are two pleurae in the body: The term tissue. Serous membranes consist of a single layer of epithelium, named mesothelium, attached to a supporting layer of connective tissue, with a small layer in between, the basal membrane (fig 1). Click the card to flip 👆. Web identify the main types of tissue membranes. Web the ventral body cavities are enclosed inside serous membranes ( serosa) that line the cavities. Serous membranes consist of a single layer of epithelium, named mesothelium, attached to a supporting layer of connective tissue, with a small layer in between, the basal membrane (fig 1). Web serous fluid secreted by the cells of the thin squamous mesothelium lubricates the membrane and reduces abrasion and friction between organs. Web the serous membrane in the drawing above. Please leave a like and subscribe! Web this video shows how to complete a draw it activity for sketching body cavities and serious membranes within the chest. Regions, subdivisions of dorsal and ventral cavity revie. Web serous fluid secreted by the cells of the thin squamous mesothelium lubricates the membrane and reduces abrasion and friction between organs. The largest part of the gut tube is ensheathed in peritoneum. There are two pleurae in the body: Web the serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth tissue membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. Microscopic observation reveals that the cells in a tissue share morphological features and are arranged in an orderly pattern that achieves the tissue’s functions. Any serous membrane will always have two parts: Serous membranes, and therefore mesothelium, line the pericardial, pleural and peritoneal cavities. This also explains the name 'serous membrane'. Three serous membranes line the thoracic cavity; Differentiate among the digestive organs and their location relative to. Web the unicellular glands are scattered single cells, such as goblet cells, found in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine. The inner layer (visceral pleura) covers the lungs, neurovascular structures of the mediastinum and the bronchi. Parietal serosa line the body cavities and visceral serosa line the outer part of the organs within the body cavity.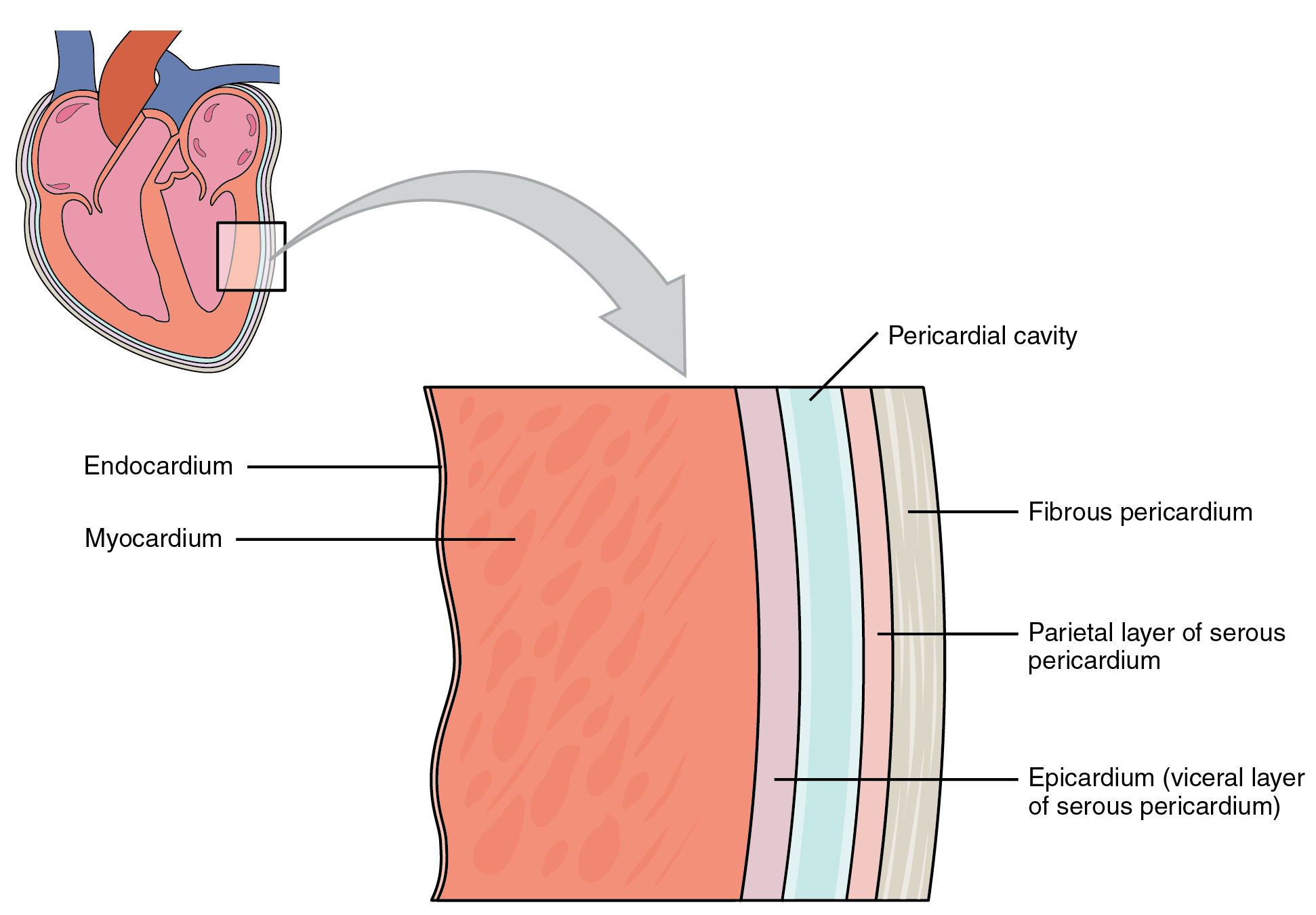
Anatomy of the Heart Medical Terminology An Interactive Approach
PPT The Human Body PowerPoint Presentation ID640744

Serous Membrane Definition, Function and Structure Biology Dictionary

Chapter 1I Serous Membranes YouTube
PPT The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac

Body Membranes Types Of Membranes In The Body Serous Membranes
PPT Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Anatomy Body Cavities & Serous Membranes YouTube
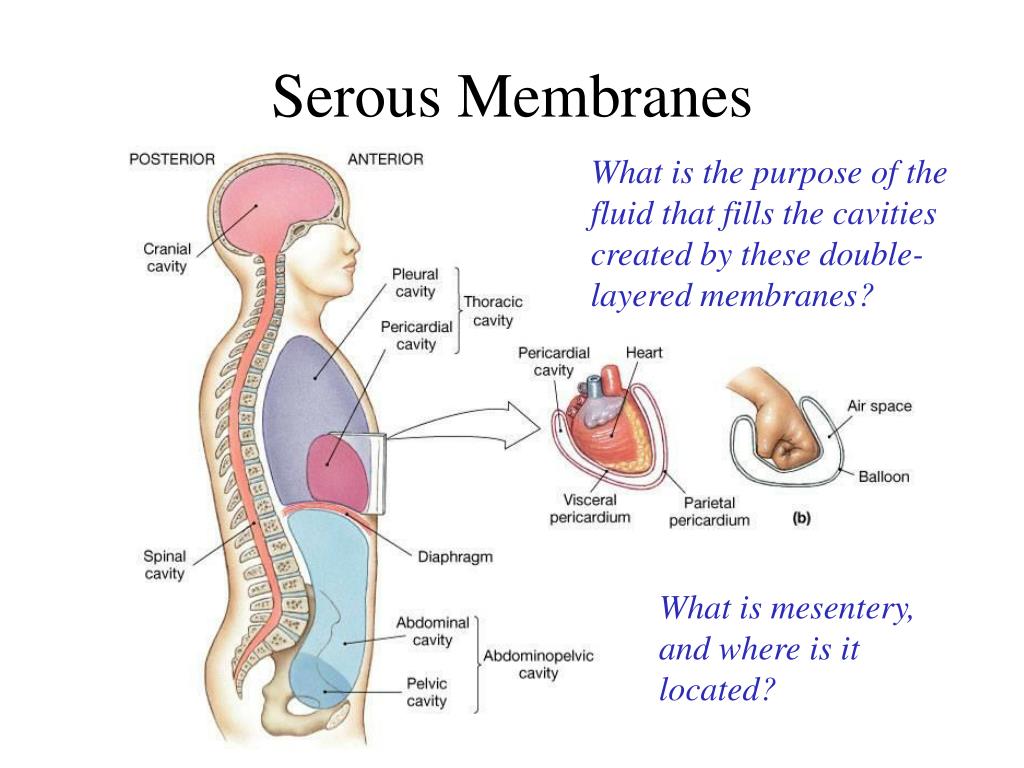
Anatomy Body Cavities And Serous Membranes Serous Membrane Membrane

serous membranes of thoracic Cavity (part 1) Diagram Quizlet
One Associated With Each Lung.
Web A Serous Membrane Consists Of A Single Layer Of Flattened Mesothelial Cells Applied To The Surface Of A Thin Layer Of Collagenous Tissue That Attaches To Underlying Endothoracic/Transversalis Fascia.
Web The Serous Membrane In The Drawing Above Is Composed Of Epithelium Which Is Always Simple Squamous Epithelium Attached To A Thin Layer Of Connective Tissue, Which Is Always Areolar Connective Tissue.
The Mesothelium Of The Serous Membrane Forms The Lining Of A Closed Serous Membrane Cavity.
Related Post: