Draw And Label A Chromosome
Draw And Label A Chromosome - Discuss the potential implications of mutations at cellular, organismal, and evolutionary levels. These paired chromosomes are called homologous. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. Start studying label the chromosome. Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. Structure and organization what is chromosomes? Describe the structure of dna and the process of dna replication. Recognize the function and products of mitosis and meiosis. Diagram illustrating the structure of a chromosome before and after the s phase. For instance, in the image below, the letters a, b, and c represent genes found at particular spots on the chromosome, with capital and lowercase letters for different forms, or alleles, of each gene. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards,. Discuss the potential implications of mutations at cellular, organismal, and evolutionary levels. Recognize when cells are diploid. Compare and. Many species have chromosomes that come in matched pairs. You've read 1 of your 10 free revision notes. Fill in the blanks with the following: These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. This page is a draft and is under active development. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like draw and label a chromosome, metacentric, acrocentric and more. Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. Web dna is the information molecule. Chromosome are the rod shape, dark stained bodies which is seen only at metaphase stage of mitosis. Web how to draw and label structure of chromosome by bio simplified Chromosome * s are long strands of dna * in cells that carry genetic information. How do they differ?, what does diploid mean? It is important to distinguish when the terms. The spindle is a structure made of microtubules, strong fibers that are part of the cell’s “skeleton.”. Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. Unduplicated chromosomes are single double helixes, whereas duplicated chromosomes contain. Its job is to organize the chromosomes and move them around during mitosis. When a cell undergoes mitosis, the chromosomes condense even further. Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. Chromosome * s are long strands of dna * in cells that carry genetic information. How do they differ?, what does diploid mean? Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. This page is a draft and is under active development. Chromosomes may exist as either duplicated or unduplicated. In these chromosomes are areas called genes that code for specific proteins. For example, humans have 46 chromosomes in a typical body cell. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, x and y, that determine our sex. Recognize when cells are diploid. It is a part of cell that carry hereditary information in the form of genes. Chromosomes may exist as either duplicated or unduplicated. Web a very long chain of dna can form a chromosome. In these chromosomes are areas called genes that code for specific proteins. Web the 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the x and y chromosomes; Many species have chromosomes that come in matched pairs. Web. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. Web each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, or “arms.” the short arm of the chromosome is labeled the “ p arm.” the long arm of the chromosome is labeled the “ q arm.” How do they differ?, what does diploid. Students label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, dna, and nucleus. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, x and y, that determine our sex. Most prokaryotic cells contain a single circular chromosome. For instance, in the image below, the letters a, b, and c represent genes found at particular spots on the chromosome, with capital and lowercase letters for different forms, or alleles, of each gene. Web this simple worksheet shows a diagram of a chromosome and where it is located in the nucleus of the cell. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. A __________ carries genetic information. Web the chromosomes start to condense (making them easier to pull apart later on). Its job is to organize the chromosomes and move them around during mitosis. All the different chromosomes of an organism make up that organism's genome. Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. Web the 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the x and y chromosomes; Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. Chromosome * s are long strands of dna * in cells that carry genetic information. This page is a draft and is under active development.
How to Draw Structure of Chromosome Labelled Diagram Structure of
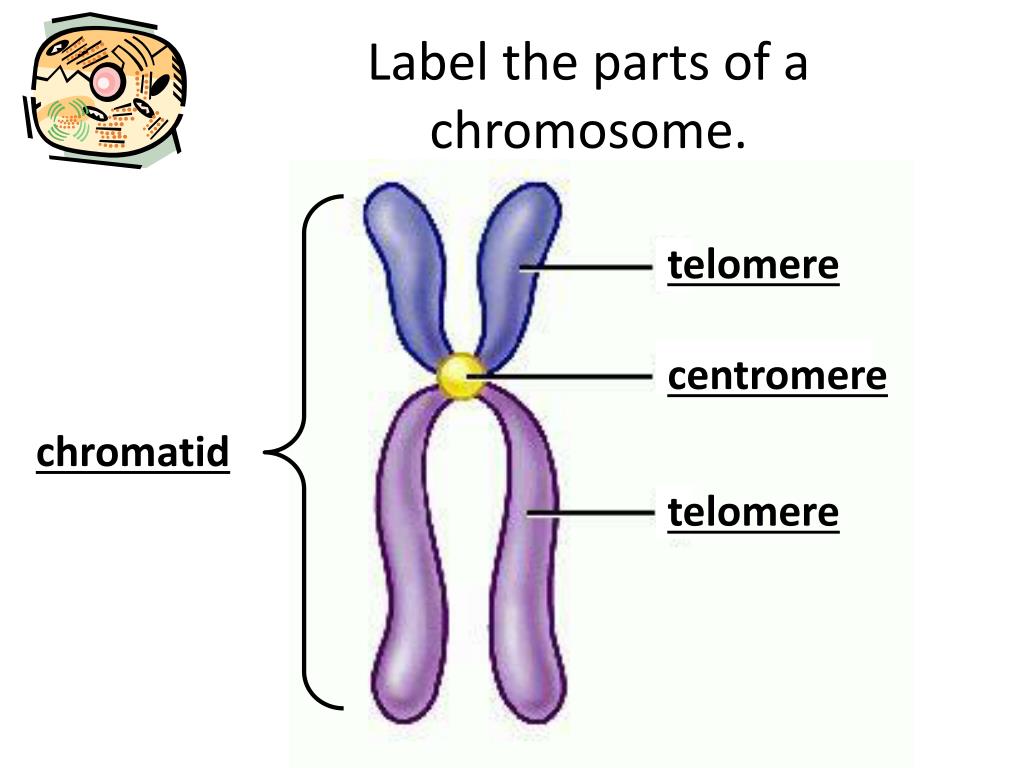
PPT Mitosis & Meiosis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2224189
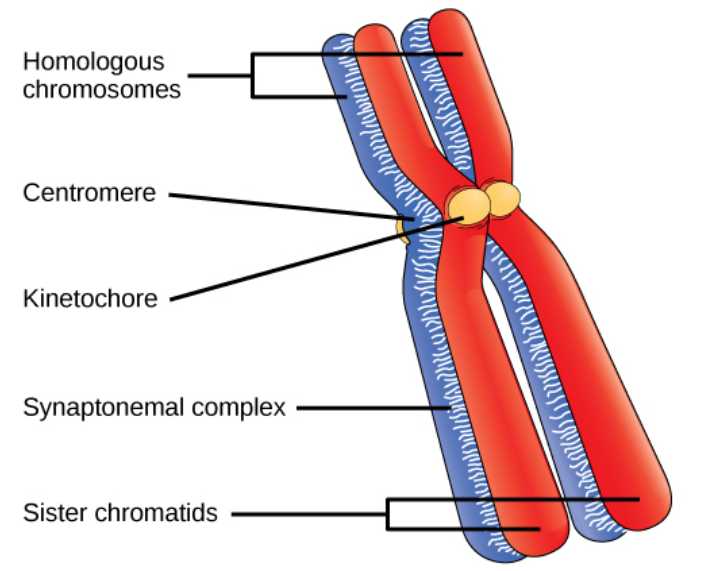
Draw the structure of the chromosome and label its parts.

How to draw Structure of Chromosome Easy Steps By Prof. Prakash Surve

Chromosome Structure, Illustration Stock Image C027/6970 Science

Parts of Chromosome Diagram Quizlet

Chromosomes Introduction, Structure & Types A Level Biology Notes

Structure chromosome infographics Royalty Free Vector Image
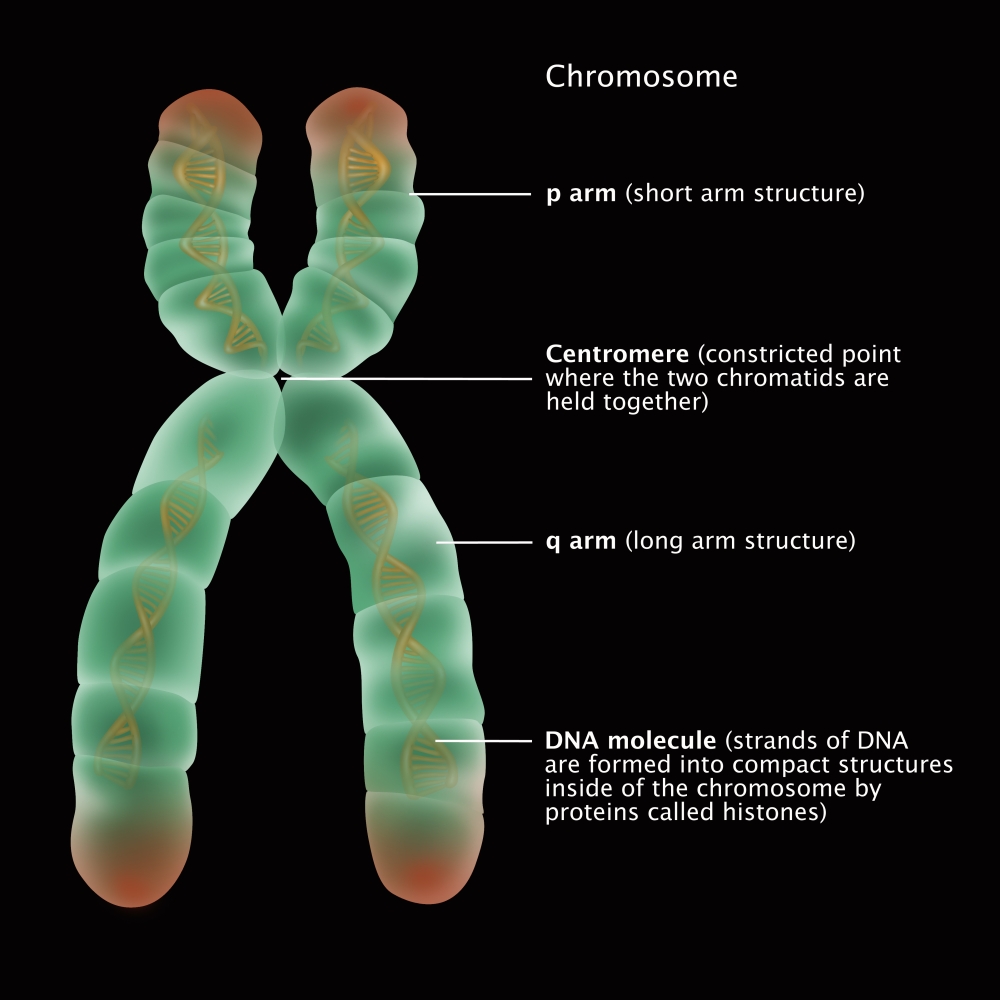
Chromosome Structure, Illustration Poster Print by Gwen Shockey/Science
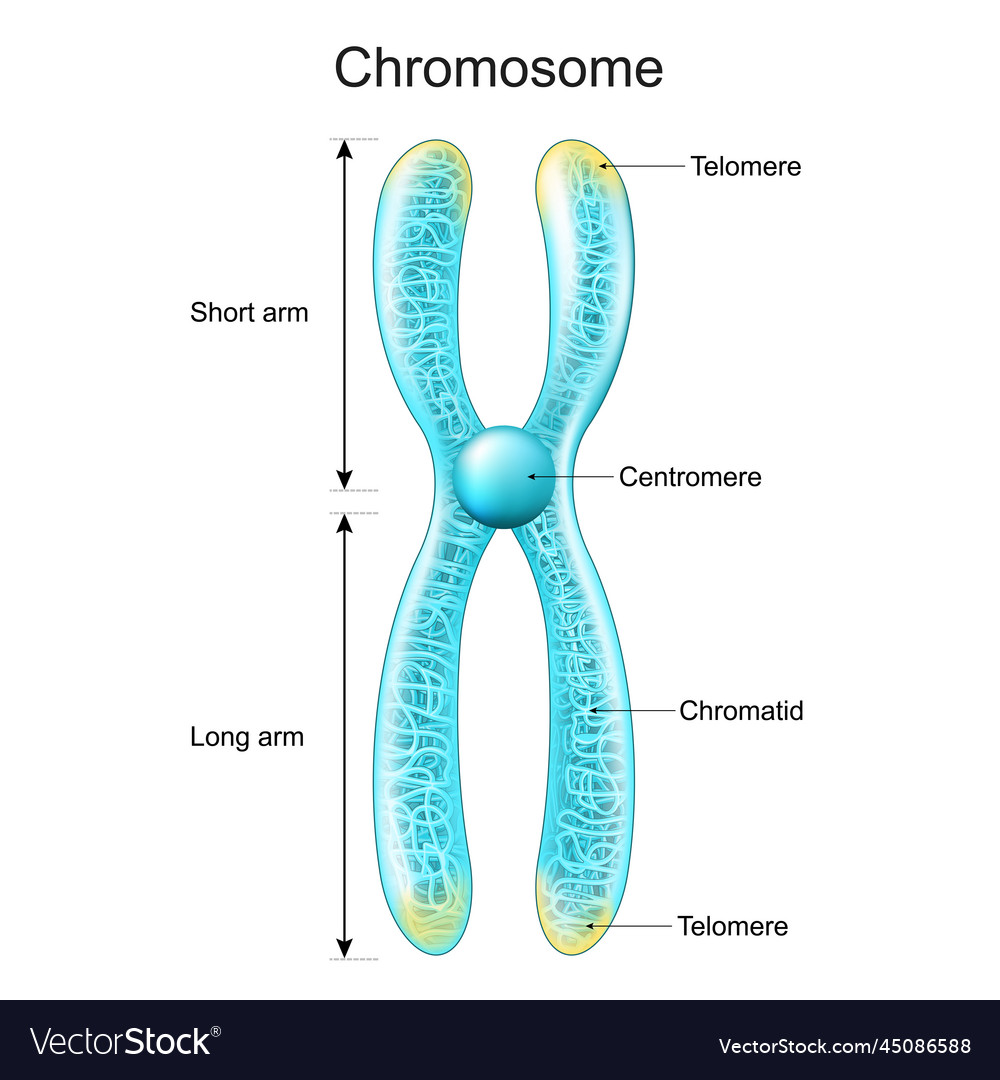
Structure of chromosome chromatid centromere Vector Image
Describe The Chromosomal Makeup Of A Cell Using The Terms Chromosome, Sister Chromatid, Homologous Chromosome, Diploid, Haploid, And Tetrad.
During Interphase Of The Cell Cycle, The Chromosome Exists In A Loose Structure, So Proteins Can Be Translated From The Dna And The Dna Can Be Replicated.
Chromosome Are The Rod Shape, Dark Stained Bodies Which Is Seen Only At Metaphase Stage Of Mitosis.
The Mitotic Spindle Begins To Form.
Related Post: